Joint Cartilage
Improvement of arthralgiaby regenerating cartilages
Block of osteoarthrosis
Regeneration of cartilaginous tissues
by suppressing inflammations of arthralgia
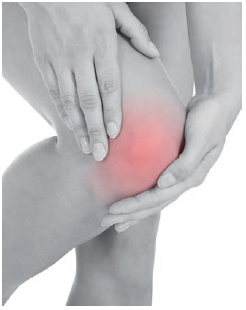
Osteoarthrosis arises with exhausted cartilage by aging and the like, which leads to arthritis or deformation to cause pain.
Ten million people above 50 years old experienced knee pain by osteoarthritis of the knee, and almost all the people by 80 years old may be influenced to some extent.
Once the articular cartilages are exhausted, it is hard to be recovered that triggers stresses in daily behaviors, and neglecting them is said to lead to an increase of the death rate.
Proteoglycan is an important ingredient to form cartilages together with collagen and hyaluronic acid that has high water retaining capacity to play a role as an articular cushion as elasticity or shock absorption.
To begin with, osteoarthrosis emerges being caused by regenerative faculty deterioration after proteoglycan decreases as we age.
And damage of cartilages breaks collagen fibers and denatures proteoglycan.
It is clarified that by intake of this proteoglycan, precursor cells of cartilages increase to regenerate cartilages and then pains are alleviated by anti-inflammatory action to improve osteoarthrosis.
Proteoglycan is expected to have effect to fundamentally improve articular disorders because it promotes metabolism of cartilages itself, which is said to be impossible for hyaluronic acid or collagen.
■Application of cartilage-derived proteoglycan for restoration of articular cartilage
Purpose
To examine if cartilage-derived proteoglycan can be a material to promote restoration of articular cartilage or not
Steps
1.Monolayer culture of rabbit cartilage cells on a proteoglycan coated culture dish
2.Three-dimensional culture of rabbit cartilage cells with proteoglycan contained atelocollagen
gel
3.Transplantation of proteoglycan contained atelocollagen gel including rabbit cartilage
cells for deficiency of rabbit thighbone condyler cartilages
4.Transplantation of proteoglycan collagen sponge for deficiency of rabbit thighbone
condyler cartilages
Result
With monolayer culture, cartilage cells aggregate formation enhancement was seen.
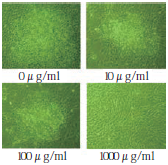
With three-dimensional culture, cartilage cells surrounding glucosaminoglycan accumulation promotion and aggrecan revelation promotion were seen.
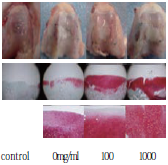
With gel transplantation including cartilage cells, stainability of recovered cartilages in 100μg/ml group was better than other groups.
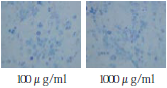
Summary
・Depending on proteoglycan concentration, differences between cartilage cells condensation formation, aggrecan gene revelation and recovery of cartilage deficient part were seen.
・Proteoglycan has a function to suppress cell adhesion, which may have influenced.
・It is possible that proteoglycan itself controlled cartilage cells increase or differentiation.
・Detailed action mechanism is not yet clear, but it will be clarified in future studies.
・Depending on the usage, proteoglycan has a possibility to be a useful medical material future studies.
Are you interested in Proteoglycans?
If you want to get it, visit this page.